The Long-Lived Cyclicality of the Labor Force Participation Rate
Abstract
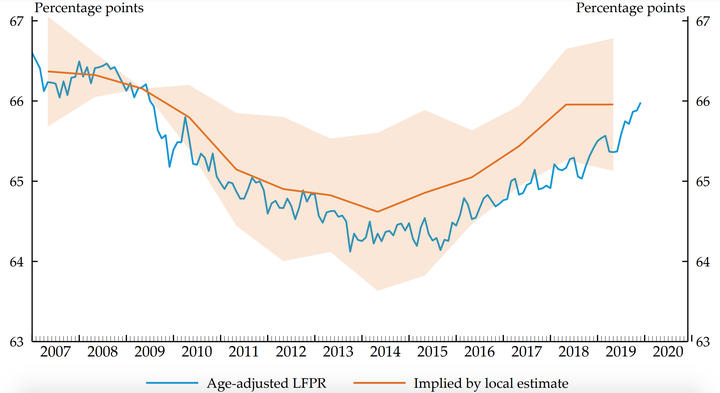
How cyclical is the U.S. labor force participation rate (LFPR)? We examine exogenous state-level business cycle shocks, finding that the LFPR is highly cyclical, but with significantly longer-lived responses than the unemployment rate. After a negative shock, the LFPR declines for about four years—substantially lagging unemployment—and only fully recovers after about eight years. Our main specifications use age-sex-adjusted LFPR, and we show that using the unadjusted LFPR is problematic because local shocks spur changes in the population of high-LFPR age groups. LFPR cyclicality varies across groups, with larger and longer-lived responses among men, younger workers, less-educated workers, and Black workers.
Type